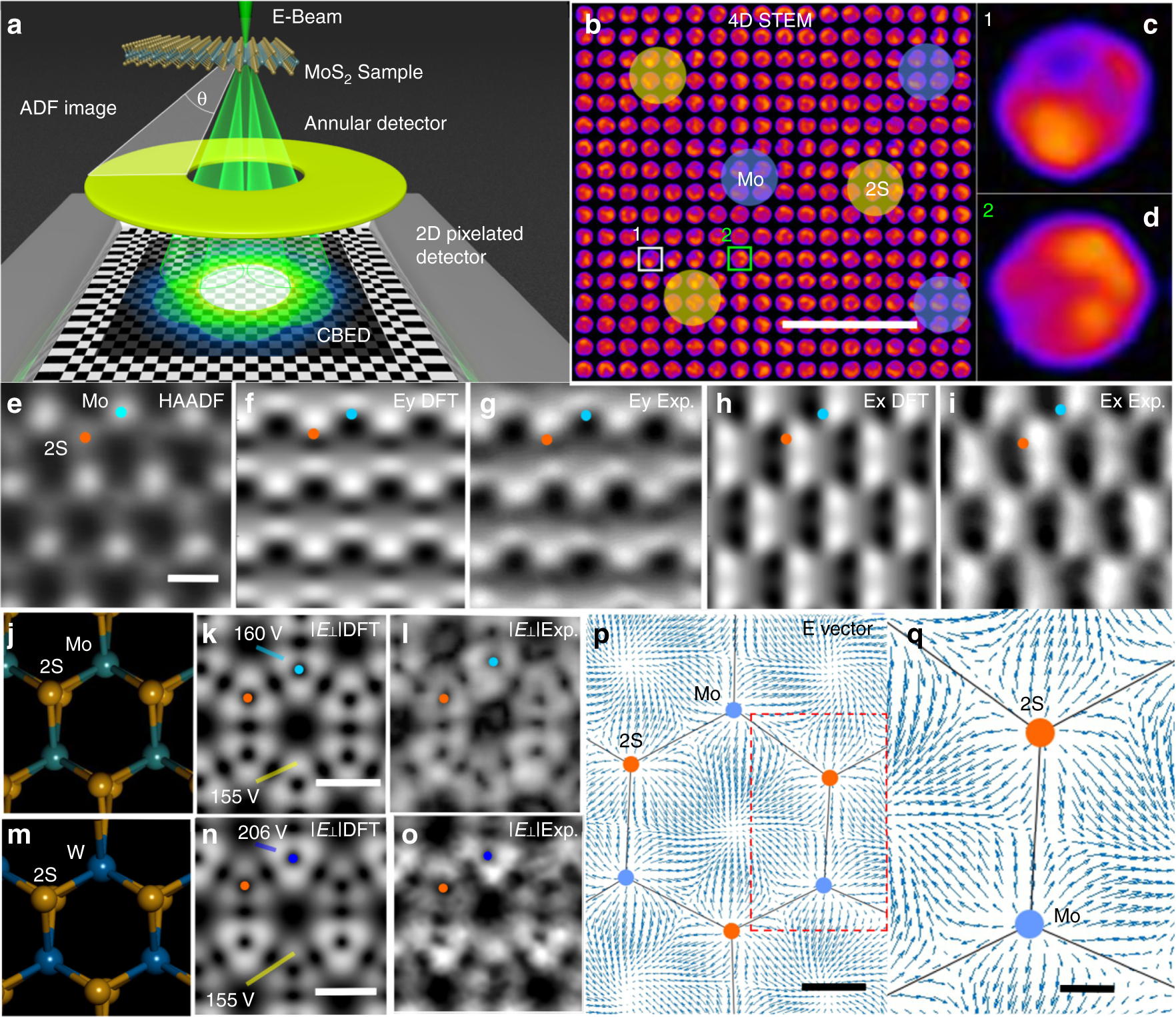
Atomic electrostatic maps of 1D channels in 2D semiconductors using 4D scanning transmission electron microscopy | Nature Communications
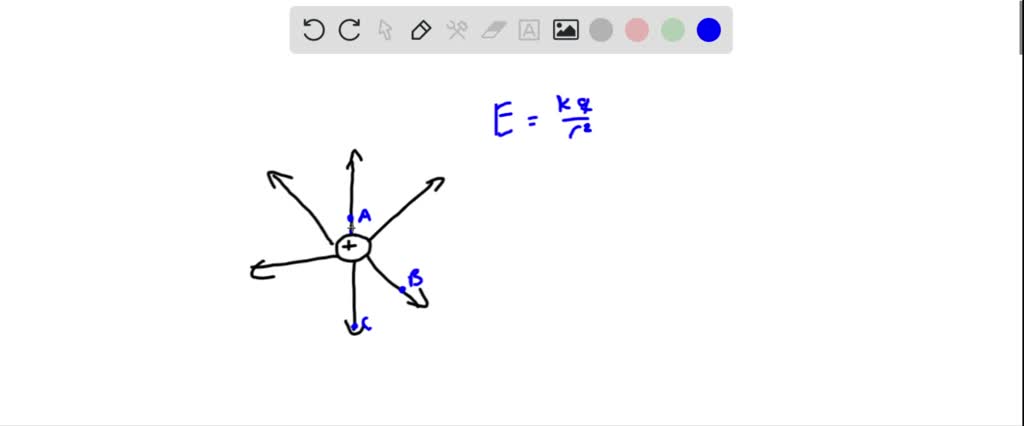
SOLVED:The diagram below shows some of the lines of electric force around a positive point charge.The strength of the electric field is (A) greatest at point A (B) greatest at point B (

SOLVED: An electric charge produces an electric intensity of 500N/C at a point in air. If the air is replaced by a medium of dielectric constant 2.5, then the intensity of the

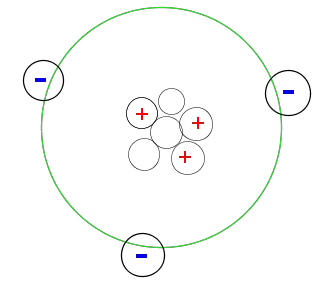
An early model for an atom considered it to have a positively charged point nucleus of charge Ze , surrounded by a uniform density of negative charge upto a radius R .

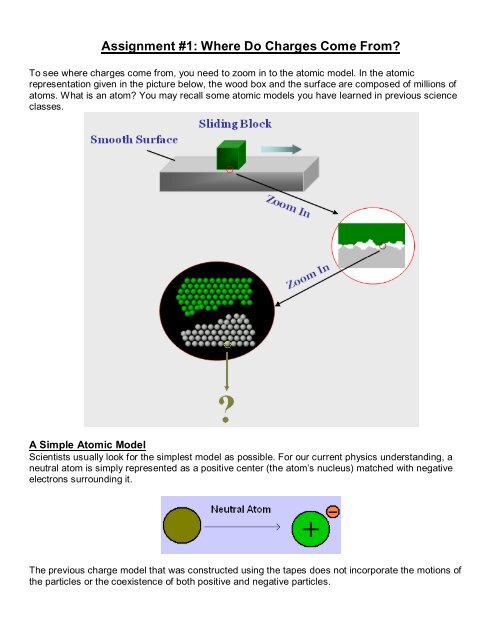
Ions. Atoms are electrically neutral, that is, they have the same number of protons (+) as electrons (-). However, atoms are most stable when their valence. - ppt download

Atomic Structure. What is an atom? An atom is an electrically neutral, spherical entity. It is comprised of a positively charged nucleus surrounded by. - ppt download

Boosting the performance of single-atom catalysts via external electric field polarization | Nature Communications
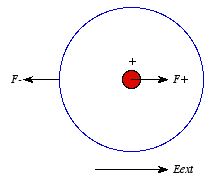
Why does an electric dipole in a uniform electric field experience only a torque and no net external force in general cases? - Quora

Effect of electric field intensity on electrophoretic migration and deformation of oil droplets in O/W emulsion under DC electric field: A molecular dynamics study - ScienceDirect
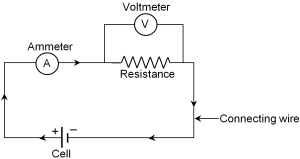
Properties of Electric current, Simple electric circuit, Current intensity & Potential difference | Science online